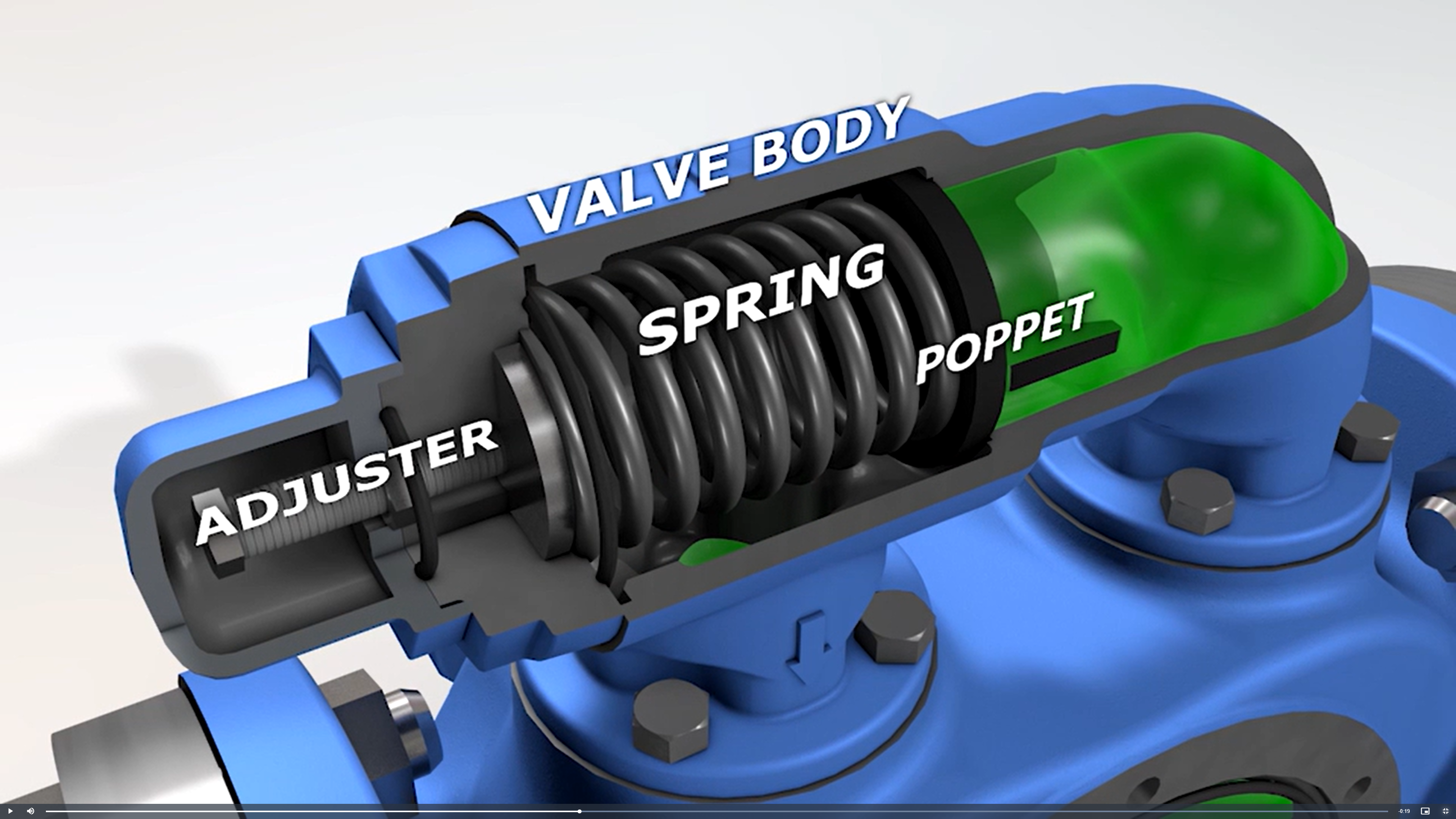
Pressure Relief Valves: Critical to Pump and System Safety and Reliability
A key advantage of rotary positive displacement pumps is providing consistent flow regardless of changes in liquid viscosity or differential pressure. But should a downstream blockage occur, pressure will rapidly build and may exceed the rating of the pump, drive equipment, system, or any combination thereof, with the potential for damage and unplanned downtime. For this reason, overpressure protection must be used, and pressure relief valves are the most commonly used form of overpressure protection for rotary positive displacement pumps.

How An Internal Gear Pump Works
Explore how internal gear pumps work, their unique “gear within a gear” design, and key advantages like efficiency and versatility. Ideal for professionals in fluid handling industries.

PUMP CAVITATION: THE SYMPTOMS, CAUSE, DIAGNOSIS, AND CURE
Customers don’t ask me to listen to quiet pumps. This is symptom #1 of a cavitating pump. The pump is loud. Descriptors like “growly”, “rumbling”, or “gravelly” are used to describe the atypically loud sound coming from the pump.
“Does it always sound like this?” I ask.
“No, it was fine in the fall, but it’s been loud all winter.”

Relief Valves: The ever-vigilant heroes
Millions of homes around the world are fitted with water heating devices such as boilers or water supply heaters. Should they overheat, pressures can rise internally until the tank ruptures. Though extremely rare, this does happen and can even propel a water heater like a rocket through the floor and roof of a dwelling. So how can we sleep peacefully each night with the knowledge that a potential catastrophe lurks in the basement?

It Flows Both Ways: a guide to running an internal gear pump in reverse
One of the biggest limitations of a traditional centrifugal pump is its inability to reverse the direction of flow. By design it can only be run in one rotation and one direction of flow. Liquid enters the eye of the impeller at the suction port (typically on the front of the pump), is pushed out radially, and exits the pump at the discharge port (typically on top of the pump). For most centrifugal pumps the suction port is larger than the discharge port to better feed liquid into the pump, and to remove any confusion as to which port is “in” and which port is “out.” Rotation arrows can be found cast onto the pump or printed on the nameplate to make it perfectly clear that these pumps run in one direction of rotation and one direction of flow.

Banana Pumps and Star Gears: A guide to pump industry slang
A gentleman once contacted me to let me know that he’d cracked a head, an impressive, but not entirely unheard-of feat. When I asked how this had happened he admitted “well, I was wailing on it pretty hard”; I appreciated his honesty. What followed was a 30-minute conversation full of mis-assumptions and confusion. At the conclusion I discovered that he was not talking about a head (as in the end plate of a gear pump) but rather a head (as in the top of a snare drum). An internet search for “head” had landed him on our site by mistake.

Pressure & Vacuum Pumping Application Concerns
In the world of gear pumps, it is common to have liquid handling applications where pressure and vacuum are of concern. So, we wanted to share our perspective and recommendations, to help with making pump choices and decisions for the various pressure and/or vacuum scenarios you may encounter.