How do lobe pumps work?
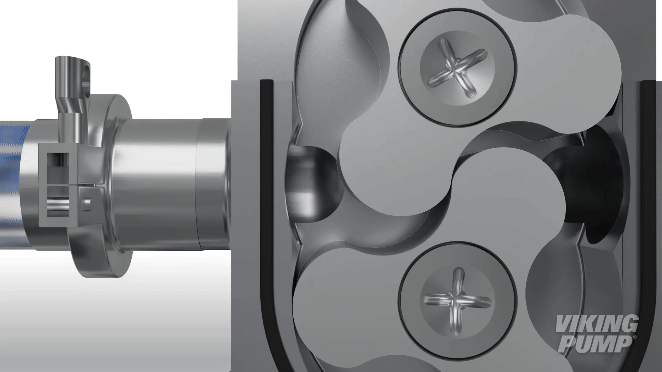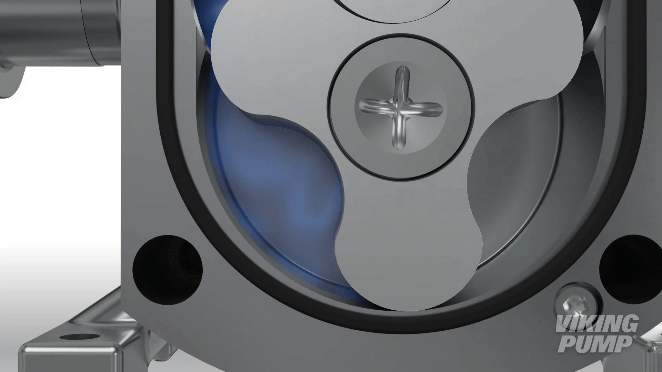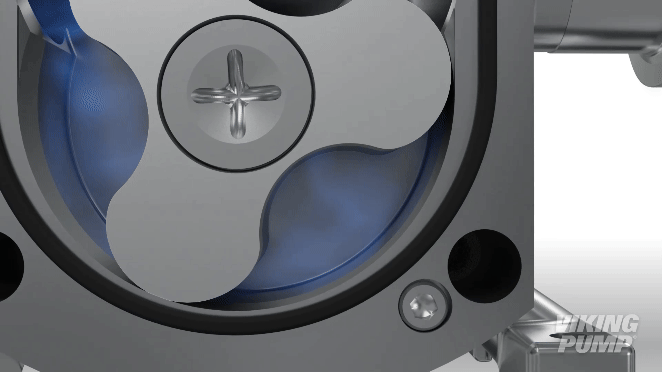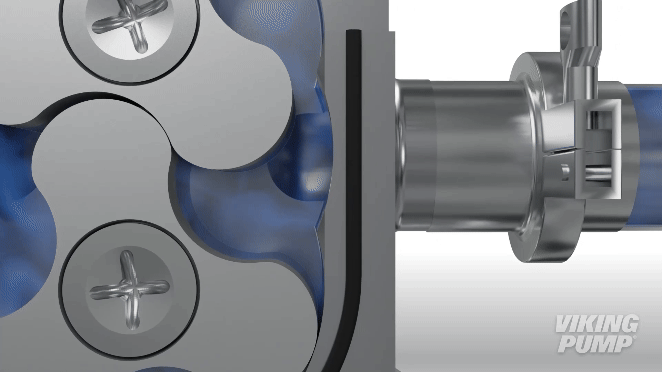
Lobe pumps are similar in pumping action to external gear pumps but differ in that the rotors are driven independently on 2 rotating shafts. A pair of external timing gears ensure that the rotors do not contact.
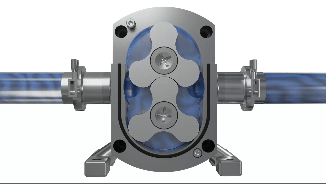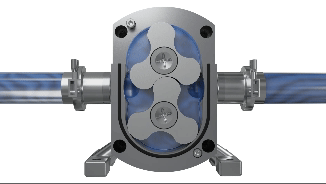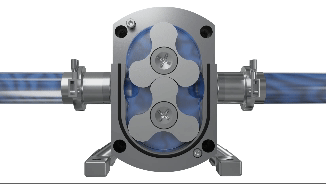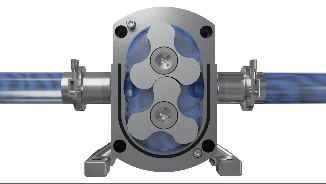
As the rotors turn, a cavity is formed at the inlet side of the pump. This creates a vacuum to pull the liquid into the spaces between the tips of the lobes. This liquid is trapped between these lobes and the close-fitting casing wall. The rotation of the rotors carries the liquid around to the outlet side of the pump. The liquid does not pass between the rotors.
At the outlet, the meshing of the lobes forces the liquid through the outlet port.